
程序设计实践 Week2 解题记录
前言
Week 2 的题目强度略大, 到周三才推完.
光是学习 Dancing Links 就花了大半天时间.
和 Week 1 不一样, 刷完 Week 2 的题后是真的挺有成就感.
1. 英杰们的蛋糕塔
传送门 -- 洛谷 P1731 [NOI1999] 生日蛋糕题意简述
给定两个个整数
- 从下往上, 圆柱体的半径
与高 均严格递减. - 圆柱体的总体积等于
.
在满足上述条件下, 最小化这所有圆柱体的侧面积之和 + 最大圆柱体的底面积. 记表面积为
数据范围:
Solution
搜索题.
为了便于描述, 我接下来说的 体积、面积, 都是指除以
从下往上搜和从上往下搜应该都可行, 我选择了前者.
既然是搜索, 对于每一层, 我们都需要去尝试所有可能的
显然
所谓缩小范围, 就是明确
假设当前层数为
根据半径和高都递减的条件, 首先肯定有:
再假设第
这个范围还是太大了, 为了进一步缩小
而 “凑出上面每层所需最小体积” 就是, 第一层半径和高都为
把 “凑出前min_v[i], 显然这个时候它们贡献的侧面积也最小, 记为 min_s[i] , 它们的计算方式为:
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){ |
接下来考虑剪枝.
- 如果
V + min_v[dep] > n, 说明不可能凑出体积, 剪. (可行性剪枝) - 如果
S + 剩下能凑出的最小面积 >= ans, 说明这种情况不可能比答案更优, 剪. (最优性剪枝)
首先, 剩下能凑出的面积 有个稳定的下界: min_s[dep].
其次, 由数学知识容易知道, 在已知剩下部分的体积的情况下, 我们可以估算出剩下部分的最小侧面积.
然后, 就是 DFS 入口的确定, 也就是估计第
这里我一开始以为要二分 , 但还是先考虑了如下非常宽松的情况:
- 令
得到 的一个上界 . - 令
得到 的一个上界 .
还好, 这样就能通过.
公式的推导都写得很详尽了, 代码就不给注释了.
AC Code:
/* |
2. 击杀黄金蛋糕人马
题意简述
给定一个
数据范围:
Solution
在看数据范围之前, 我就想到了一种时间复杂度非常优秀的做法: 二分最小面积, 看切出它的最小刀数是否小于
一看checker 呀,
记 f[w][h][m]: 把
然后, 思考怎么拆分子问题.
很容易想到, 可以枚举下刀的位置, 以及分为两大块后, 左右两块各应该再切成多少块.
边界情况:f[w][h][m]
一共
AC Code:
|
3. 寻找林克的回忆(1)
传送门 -- 洛谷 P1784 数独题意简述
给定一个
Solution
数独有row[r][d], col[c][d], block[b1][b2][d] 这三个 bool 数组来记录数字
其中, 可用
然后就是普通的 DFS 了.
时间复杂度最坏为
AC Code:
|
4. 寻找林克的回忆(2)
传送门 -- 洛谷 P10481 Sudoku 传送门 -- 洛谷 P10482 Sudoku 2题意简述
给定若干
上一题的
Solution
爆搜代码过不了, 就需要找优化方法.
原来的爆搜代码, 是按从上到下, 从左到右的顺序依次填数.
假如是人来做数独, 人会怎么做?
我不知道别人是怎么做的, 反正我会先把所有能唯一确定的空先填上, 然后再找候选数最少的空进行尝试, 这样做是有道理的, 比起按顺序填数, 这种做法能够大大减少需要尝试的情况数.
这种搜索方式就是启发式搜索, 虽然最坏时间复杂度和原来一样, 但平均时间复杂度能减少到
为了高效找到候选数最少的空, 我们不再使用原来的 row, col, block 二维 bool 数组, 而是使用bitmask: 用二进制数描述每个数的使用情况.
具体来说, 就是用十位二进制数
于是, 就可以用 row[i] 表示第col[j] 表示第block[b1][b2] 表示第
然后使用位运算高效完成这些基本操作:
(mask 是一个十位二进制数, d 是数字
| 操作 | 对应位运算 |
|---|---|
| 数字 | mask >> d & 1 |
| 标记 | mask |= 1 << d |
| 标记 | mask &= ~(1 << d) |
| 三个 masks 取并 | row[i] | col[j] | block[b1][b2] |
显然, 行、列、宫格三个十位二进制数取并后得到的 mask, 就标志了该位置的数字使用情况,__builtin_popcount 求出
AC Code:
|
5. 寻找林克的回忆(4)
题意简述
给定若干
上一题的
Solution
读完上题的 Solution 就可以发现, 我上一题在代码实现部分偷懒了, 我并未把所有能唯一确定的空先填上, 而只是找了候选数最少的空进行尝试, 每层搜索只填一个数, 自然不够高效.
换言之, 我们需要准确实现这个过程: 先把所有能唯一确定的空先填上, 然后再找候选数最少的空进行尝试.
需要注意的是, “能唯一确定的空” 是相对当前状态而言的, 如果上层搜索所作出的猜测不正确, 那么我们填入的这些 “能唯一确定的空” 就也需要回溯.
要如何优雅地实现 “启发式回溯” 呢?
很简单, 和普通的搜索回溯一样, 这里也是要 “撤销” 作出的操作, 唯一的区别就是操作可能不止一次, 自然想到用一个栈来记录所有填能唯一确定的空的操作, 并在开始填这些空时记录原来的操作栈的大小, 就可以在搜索失败后依次还原这些操作了.
Implementation:
|
但, 还没有结束.
这份代码 TLE 了.
最令我伤心的是, 我花了一个晚上 Debug 它 (虽然好像没bug), 最后才发现是因为剪枝还不够强 (sad).
在这份代码上花了太多时间, 所以尽管它没能 AC , 我还是要把它贴出来.
那么这份代码为什么无法通过呢?
因为, 我只考虑了考虑了一个空只能填一个字母的情况, 没考虑一个字母只能填在某个空的情况.
比如, 在某一行中, 有个空可以填 C 和 F, 其它空都有别的可填字母, 唯独没有 F, 此时 F 就只能填在这个空.
这是个非常强力的剪枝, 也是现实数独中常用的解题技巧, 但我在写代码时却没考虑到.
修改后的代码如下:
bool dfs(int filled){ |
这份代码只得了
啊? 这都过不了?
冷静思考了一下, 用for 循环去找只可填在 1 个空的字母 , 效率肯定低 (但我真的以为这个常数可以忽略不计呀呜呜). 需要更极致的优化.
稍微动一下脑筋, 其实我们可以用两个掩码 once 和 twice 分别记录出现某一单元 至少出现twice |= (once & s), 再更新 once |= s, 遍历结束后, once & ~twice 就是只出现
利用这个trick可以减少一重循环 .
于是这个优化到可能只有正在写这篇题解时的我才能看懂的最终版本它来了:
bool dfs(int filled){ |
折腾了一个晚上, 最终才以
还是太菜了呜呜呜.
6. 寻找林克的回忆(4) [DLX]
题意简述
Solution
这里默认读者已经会用 DLX 求解 01 精确覆盖问题 . 相关内容我已在博客的另一篇文章详细介绍, 这里不做赘述.
首要问题是把数独问题转化为 01 精确覆盖问题.
用三元组
- 行-数字约束: 第
- 列-数字约束: 第
- 宫-数字约束:
- 唯一性约束: 格子
又因为
又因为
于是,
具体应该怎么进行呢?
在读入之前, 先插入所有的
然后, 在读入
最后, 再调用dance函数进行搜索求解.
AC Code:
|
这份代码比上一题的 DFS 快, 只用了
7. 寻找林克的回忆(3)
传送门 -- 洛谷 P1074 [NOIP 2009 提高组] 靶形数独题意简述
给定一个
- 正中心的格子为
- 最外面一圈的格子为
示意图:
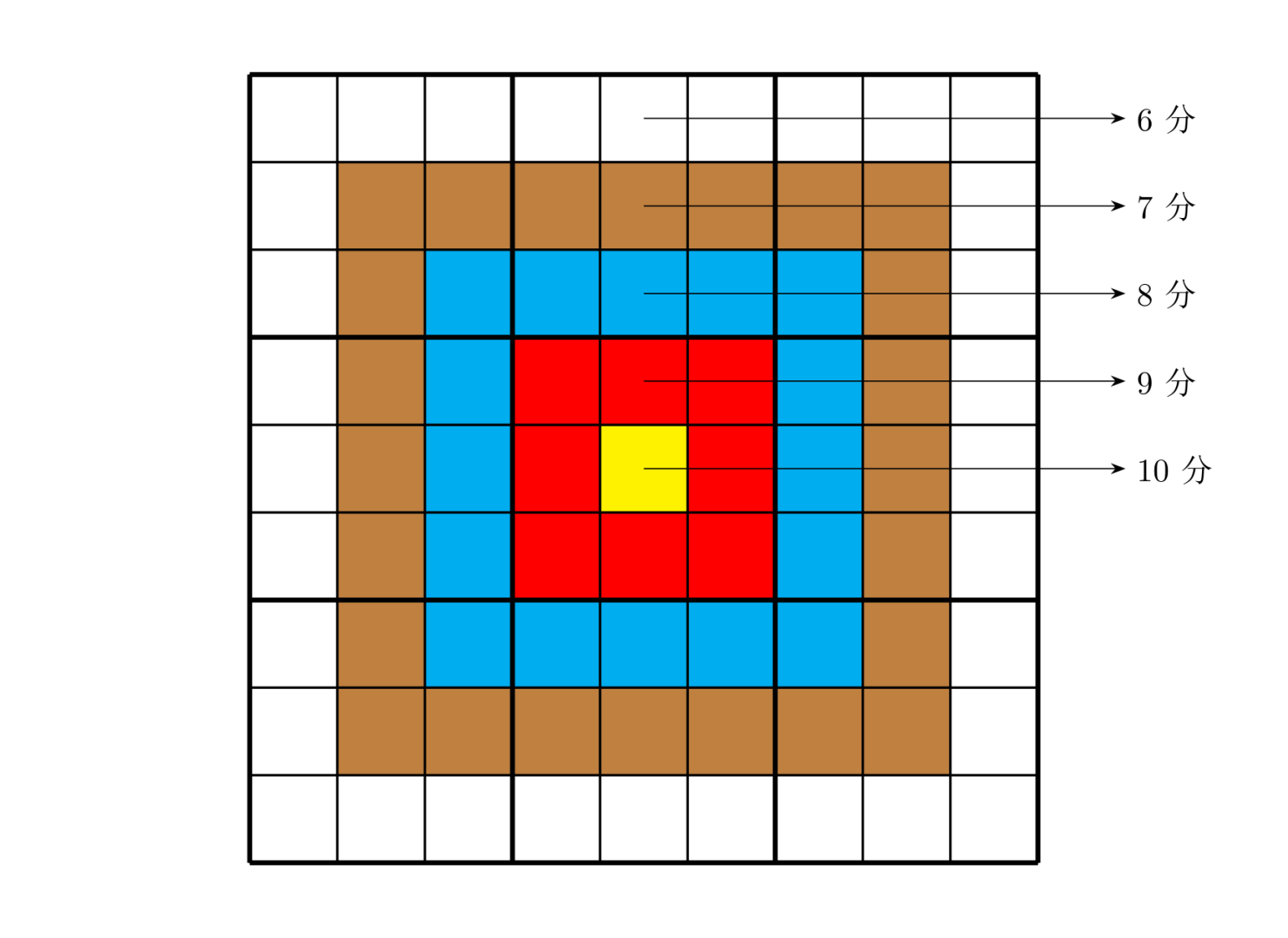
总分值为每个方格的分值和填在格子中的数字的乘积之和, 即
Solution
使用目前最快的 DLX 算法来求解数独, 每得到一组可行解就更新最大得分即可.
抄抄板就行, 唯一的改动只有 dance 函数中对 right[0] == 0 的处理.
AC Code:
|
8. 滚石柱
传送门题意简述
不知道怎么简述, 所以我直接把题目搬过来了:
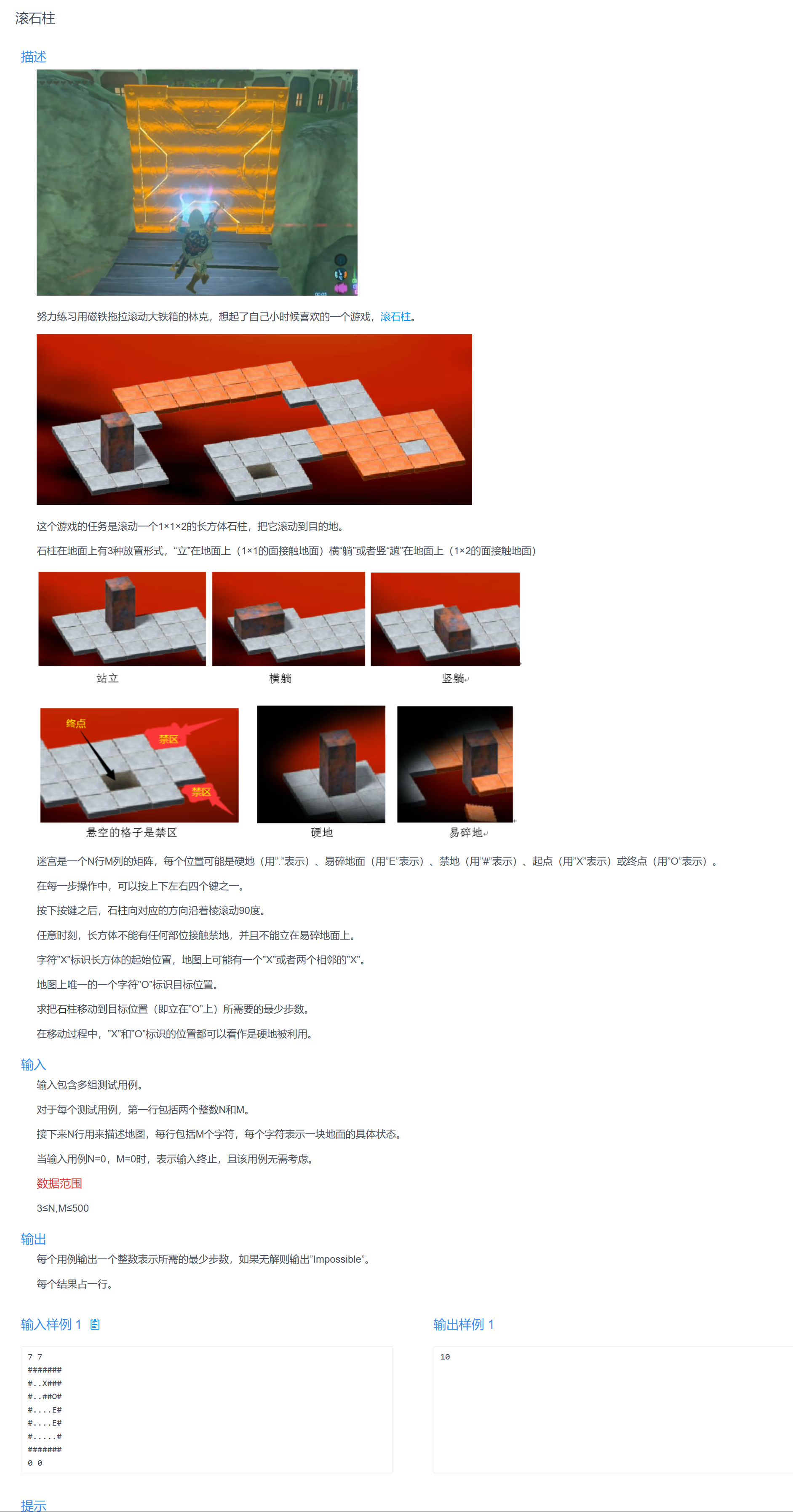
Solution
没啥思维难度, 如果像我一样是用石柱放置形式 + 一个坐标来描述石柱位置的话, 在翻转时要正确处理好下一个坐标 .
需要分好几种情况进行讨论, 代码相对繁琐.
AC Code:
|
9. 维修电路
传送门 -- 洛谷 P4667题意简述
简述不了, 进传送门看题吧.
Solution
解决此类问题的基本思想在我的博客中已有记载.
不要被洛谷的神秘标签带偏了, 这只是01 BFS.

从一个格子沿对角线可以走到其它
我们知道, BFS的层序遍历特点能保证终点第一次被访问时就是最优解, 但如果我们在遍历时同时把这
为了维护BFS的最优解性质, 我们每次:
- 把不需要转动电线的走法放到队首.
- 把需要转动电线的走法放到队尾.
再取队首拓展, 就能保证每次拓展的点都是最优解.
然后要注意格点和格子的坐标关系, 这个自己画图就懂了, 我不做赘述.
已在代码里附上错误的 DFS 代码, 可思考为什么这种 DFS 写法是错误的.
AC Code:
|
10. 最省赛程
题意简述
有
回答
初始油箱为空, 求从起点到终点所需最小花费.
若无法到达终点, 输出 impossible .
数据范围:
Solution
既有油量又有价格, 似乎是个二元问题.
考虑状态
而状态可以由这两条路径进行转移:
- 在该城市加
- 选择走油耗为
相比于普通的 Dijkstra, 我们只需要把原来表示距离的数组 dis[N] 拓展为二维 dis[C][N] 即可.
也可以换一种角度理解: 把每个点拆成
单次询问的时间复杂度为
如果所有输入都取到上界的话, 应该是过不了的, 不过我也想不到更优秀的解法了, 实测数据并没有这么强, 这样的思路是可以通过的.
AC Code:
|
- 标题: 程序设计实践 Week2 解题记录
- 作者: Coast23
- 创建于 : 2025-07-03 11:30:37
- 更新于 : 2025-07-03 14:16:59
- 链接: https://coast23.github.io/2025/07/03/程序设计实践-Week2-解题记录/
- 版权声明: 本文章采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 进行许可。
